Developing OpenWRT in QEMU with Eclipse Che
OpenWrt is a highly extensible GNU/Linux distribution for embedded devices (typically wireless routers). OpenWrt is built from the ground up to be a full-featured, easily modifiable operating system for embedded devices. You can have all the features you need with no bloat, powered by a modern Linux kernel.
We can create and develop OpenWRT CMake packages with Eclipse Che.
In this blog post, we will review developing OpenWRT in QEMU with Eclipse Che in 4 parts:
|
Note
|
In this blog post, we will use OpenWrt HelloWorld package. |
First of all, we need to create a new workspace from the repo openwrt-helloworld-package with Eclipse Che. The easiest way to do this is to use Eclipse Che hosted by Red Hat and create a workspace by navigating to the following URL - https://workspaces.openshift.com#https://github.com/che-incubator/openwrt-helloworld-package.
PART 1: Quick start with prebuild resources
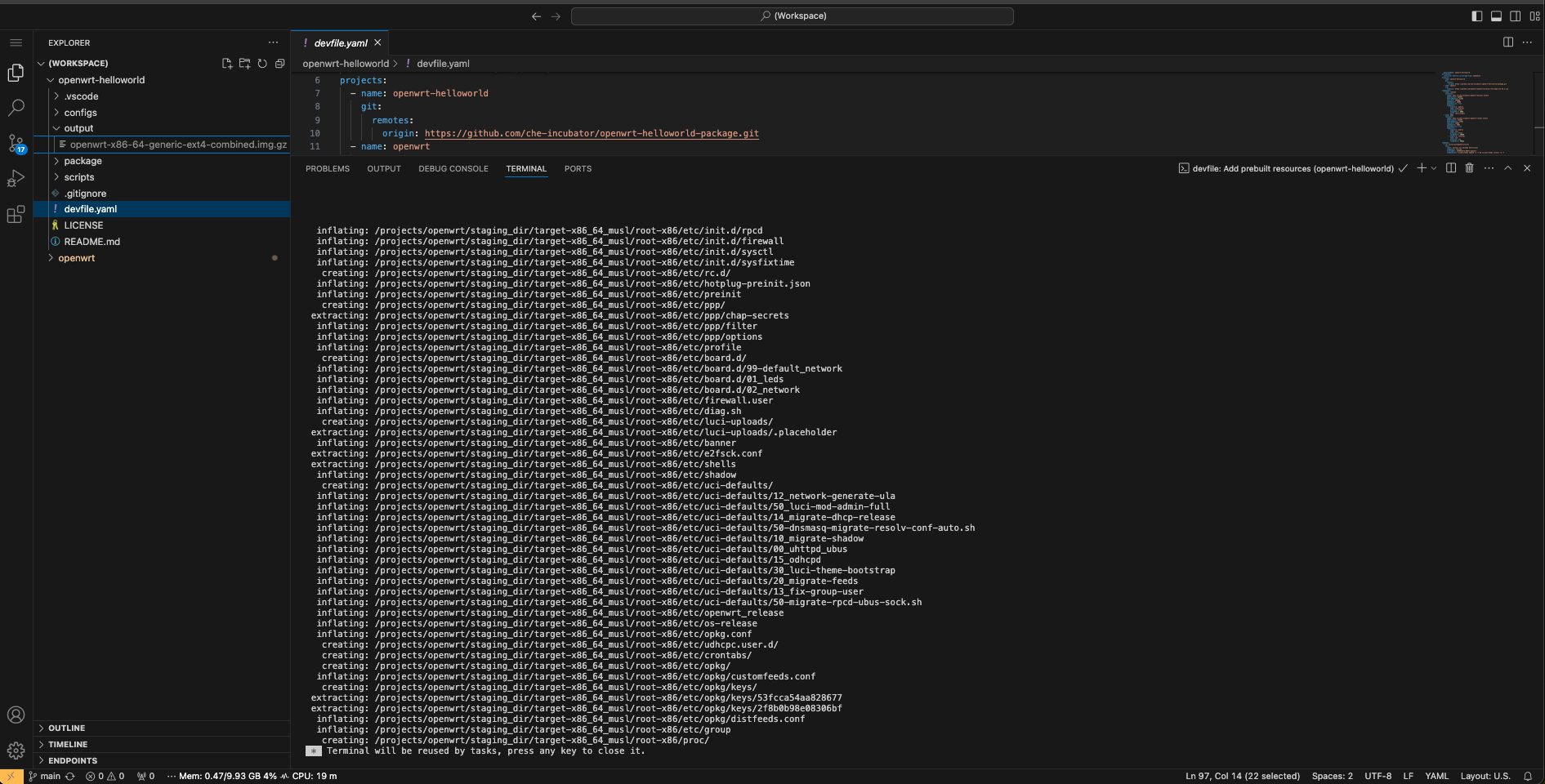
Prebuilt resources could be applied for a quick start with Eclipse Che. We could do this by running the next tasks from the devfile:
-
Add prebuilt resources
|
Note
|
After adding prebuilt resources, we should see the
openwrt-*.img.gz file in the
output directory. Prebuilt resources were
added to the runtime image during the last successful
GitHub image build action.
|
PART 2: (optional) Build all packages and the kernel
Instead of using prebuilt resources from STEP 1, we can
install all package definitions, copy
.config
file and build all packages and the kernel. We can do this
by running the following tasks from the
devfile:
-
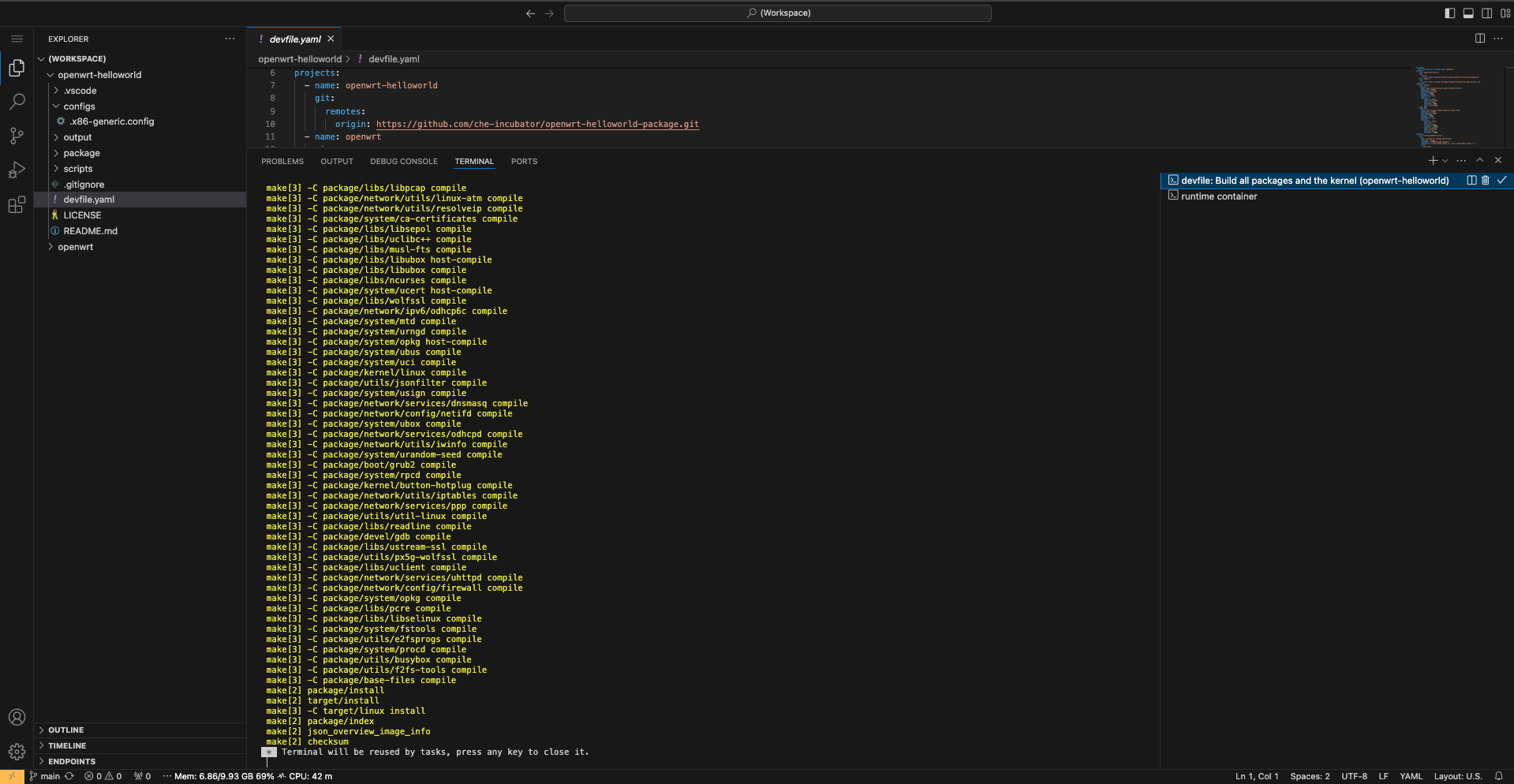
Install all package definitions -
Copy diff-config to OpenWRT -
Build all packages and the kernel
|
Note
|
The build process may take a while, which is why using
prebuilt resources from STEP 1 could be more desirable
for getting started quickly. After the build is
complete, we can see the
openwrt-*.img.gz file in the
output directory.
|
PART 3: Run OpenWRT in QEMU
After adding prebuilt resources or building all packages and the kernel, OpenWRT could be run in the QEMU VM by running the following tasks from the devfile:
-
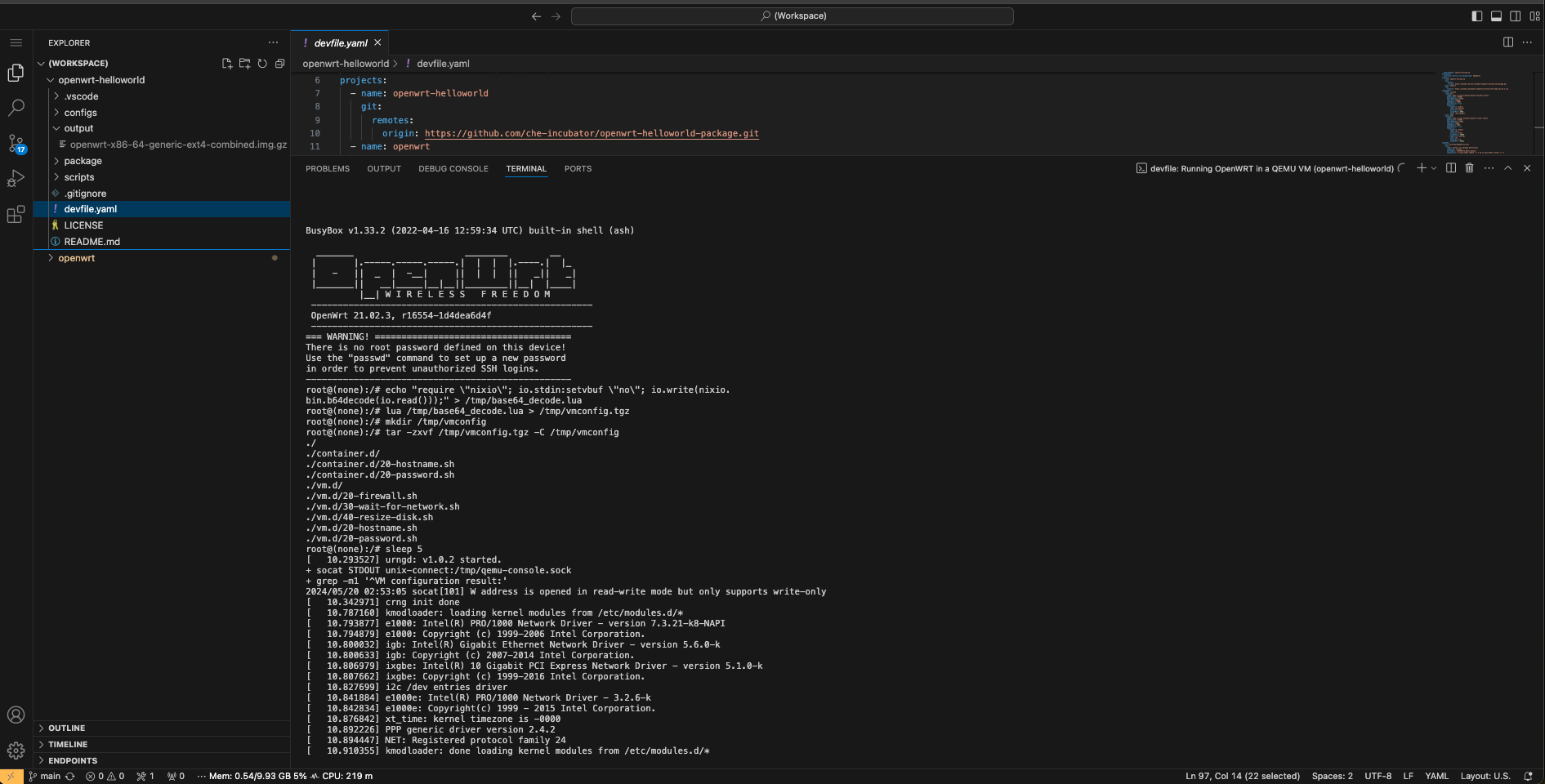
Running OpenWRT in a QEMU VM
After running the task, we see the OpenWRT booting in the QEMU machine emulator and virtualizer.
We can access the OpenWRT console by running the task
Remote access to OpenWRT via SSH and start the
helloworld package by running:
helloworld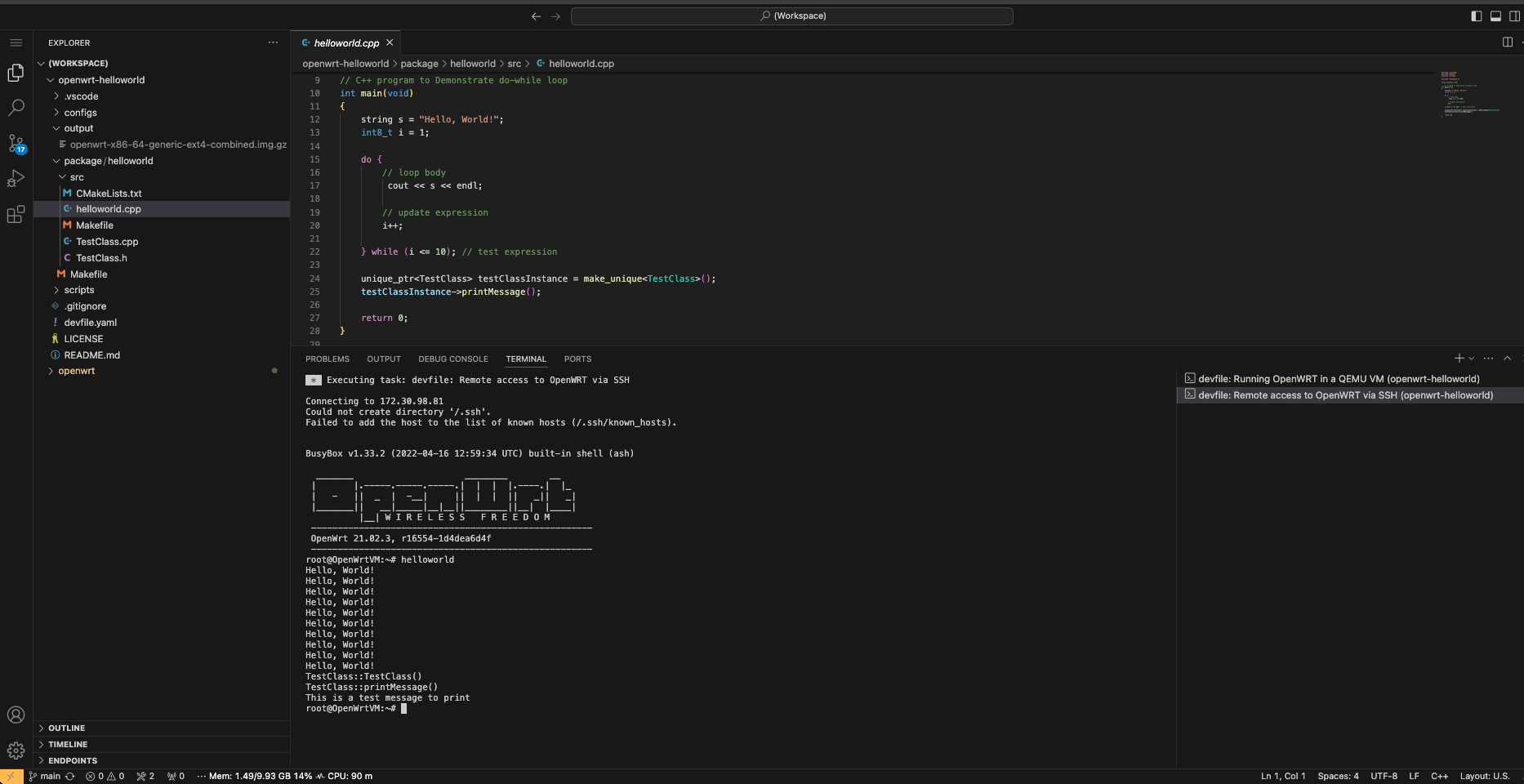
PART 4: Debugging helloworld package
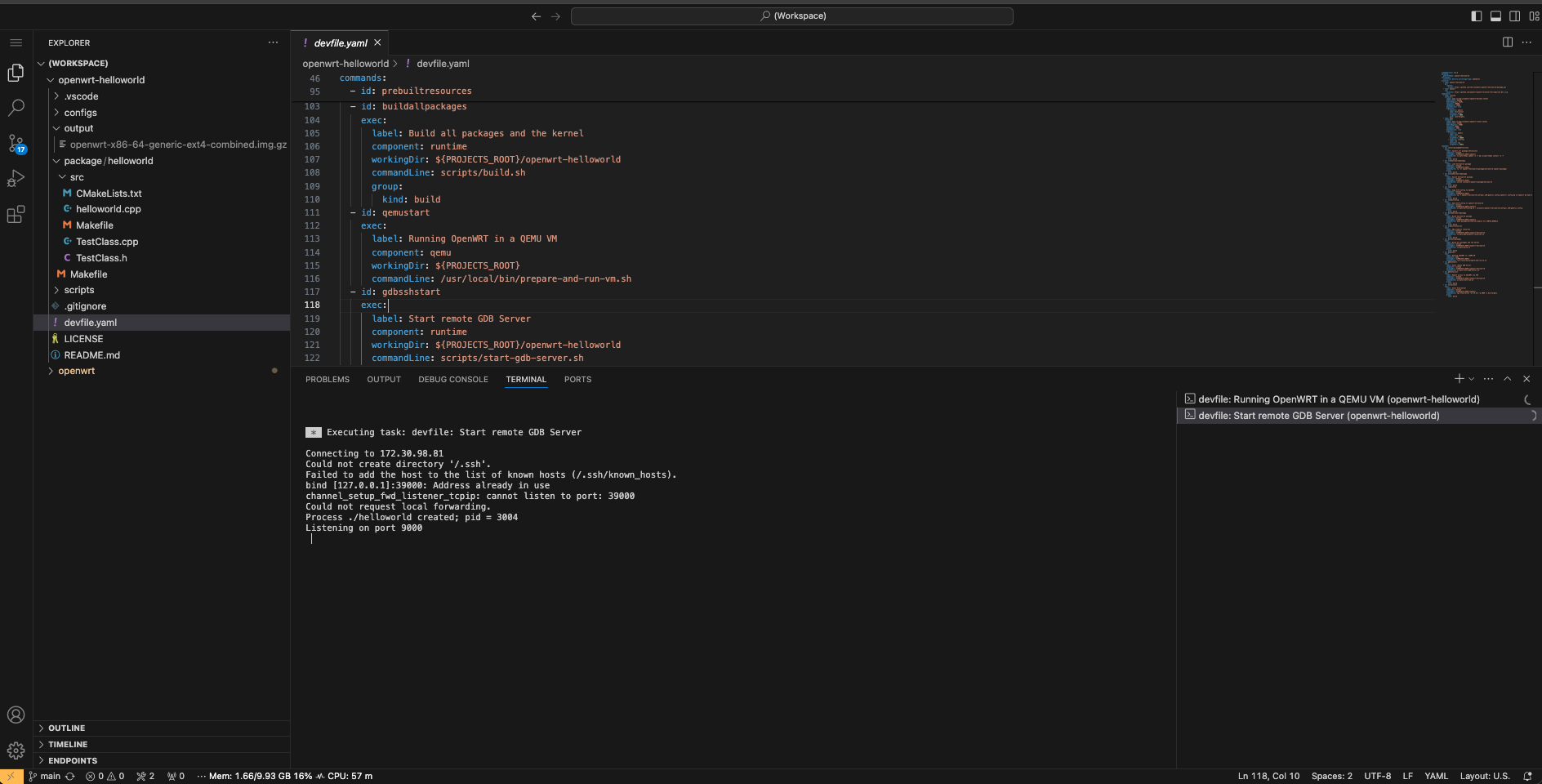
After starting OpenWRT in a QEMU VM, we need to run a remote
gdbserver for debugging. We can do this by running the task
Start remote GDB Server from the
devfile.
Then, we can debug the helloworld package with IDE:
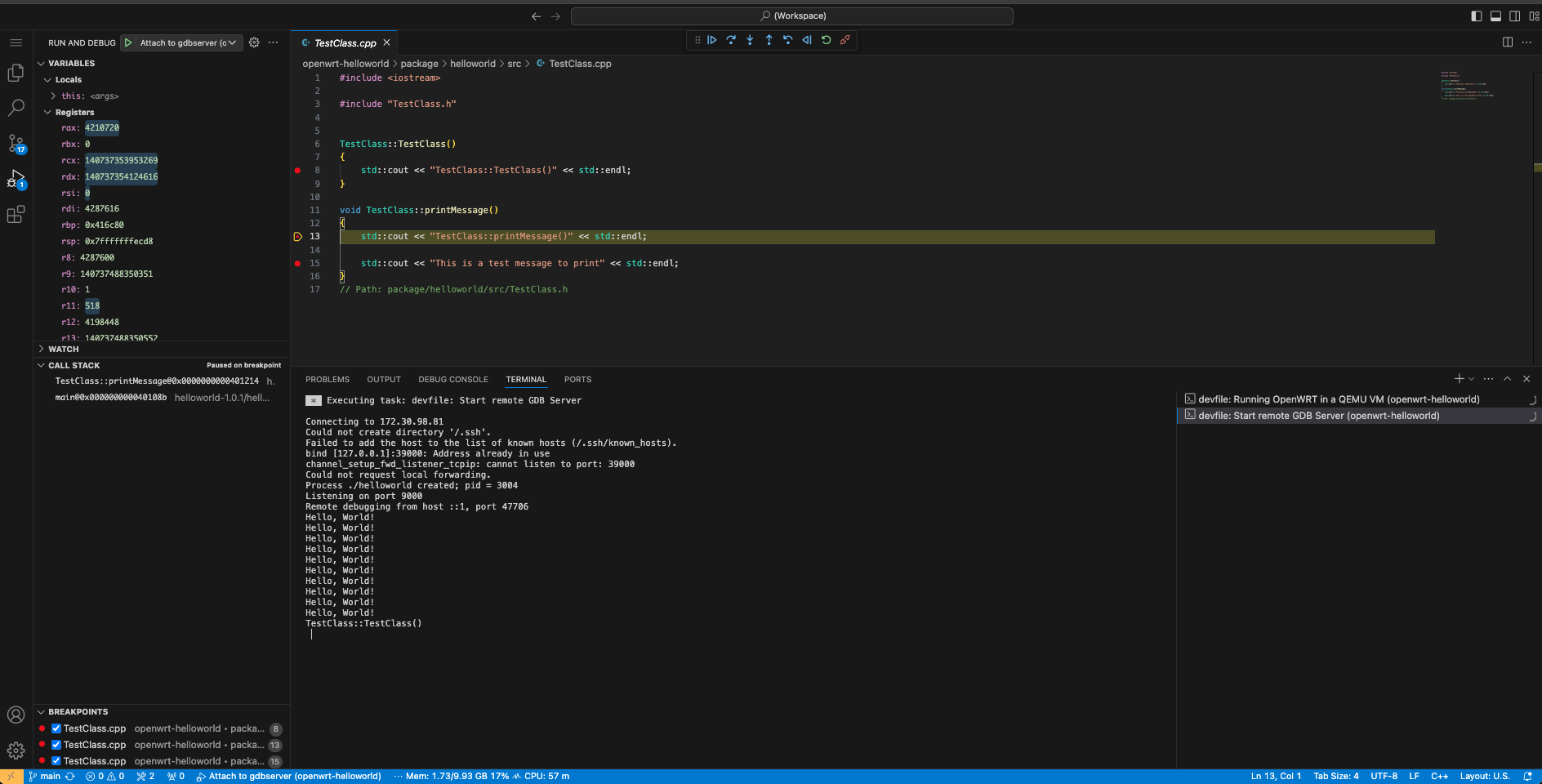
|
Note
|
The task Start remote GDB Server should be
run before each new debug session.
|
Thank you for reading. I hope you found this article helpful.